What is SVN (Subversion)?
Subversion is a free/open-source version control system. Subversion manages files and directories, and the changes made to them, over time. This allows you to recover older versions of your data, or examine the history of how your data changed. In this regard, many people think of a version control system as a sort of “time machine”.
Install SVN (Subversion) Server on Fedora 19/18/17/16/15/14, CentOS 6.4/6.3/6.2/6.1/6/5.9, Red Hat (RHEL) 6.4/6.3/6.2/6.1/6/5.9
1. Change root user
2. Install needed packages (mod_dav_svn and subversion)
Note: If you don’t have Apache installed already, this command installs it also. Read more about installing Apache and PHP >>
3. Modify Subversion config file /etc/httpd/conf.d/subversion.conf
Add following config to /etc/httpd/conf.d/subversion.conf file:
4. Add SVN (Subversion) users
Use following command:
Note: Use exactly same file and path name as used on subversion.conf file. This example use /etc/svn-auth-users file.
5. Create and configure SVN repository
Restart Apache:
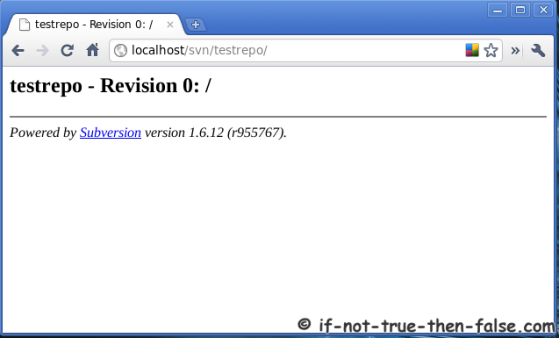
Goto http://localhost/svn/testrepo address and you should see something like following, write username and password:
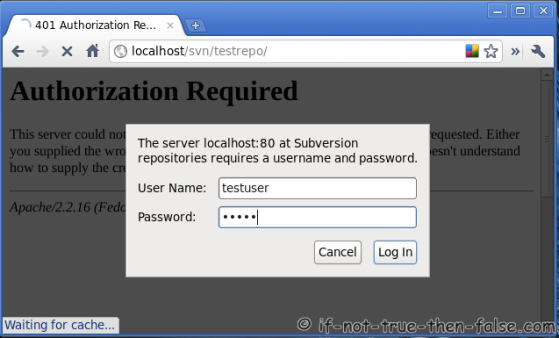

6. Configure repository
To disable anonymous access and enable access control add following rows to testrepo/conf/svnserve.conf file:
7. Create trunk, branches and tags structure under testrepo
Create “template” directories with following command:
Then import template to project repository using “svn import” command:
Check results on browser and see testrepo revision 1: